9 November 2023
- Total number of non-cash payments in the euro area in second half of 2022 increased by 8.8% to 65.9 billion compared with the previous six-month period, with total value rising by 2.8% to €118.8 trillion
- Card payments accounted for 54% of total number of non-cash payments in second half of 2022, credit transfers for 20%, direct debits for 16% and e-money payments for 7%[1]
- Number of payment cards issued in second half of 2022 increased by 3.8% to 704.8 million compared with the previous six-month period, averaging two payment cards per euro area inhabitant, with an average value of around €41 per card transaction
- Around 29.4 billion transactions processed by retail payment systems in euro area, worth €23.5 trillion
The European Central Bank (ECB) today published the statistics on non-cash payments for the first and second halves of 2022.[2] The statistics comprise indicators on access to and use of payment services, payment cards and terminals by the public, as well as volumes and values of transactions processed through retail and large-value payment systems. This press release focuses on developments in the euro area as a whole, although statistics are also published for all euro area countries and all reporting non-euro area countries. EU and euro area aggregates are also published.[3]
Payment services[4]
In the second half of 2022 the total number of non-cash payment transactions[5] in the euro area increased by 8.8% to 65.9 billion compared with the previous six-month period, with the corresponding total value rising by 2.8% to €118.8 trillion. Card payments accounted for 54% of the total number of transactions, while credit transfers accounted for 20%, direct debits for 16% and e-money payments for 7%. The remaining 2% comprised cheques, money remittances and other payment services (see annex, Table 1).
Chart 1
Use of the main payment services in the euro area
(number of transactions in billions, right-hand-side scale refers to the first and second halves of 2022)

Source: ECB.
Note: Data have been partially estimated for periods prior to 2010, as methodological changes were implemented in previous years and some corresponding data are not available. The historical estimation done by the ECB ensures comparability of figures over the entire period. Statistics were also collected for cheques, money remittances and other payment services which together accounted for 2% of the total number of non-cash euro area payment transactions in the second half of 2022.
When considering annual figures for non-cash payment transactions in the reference year 2022, the total number of transactions increased by 10.9% to 126.6 billion compared with 2021, and their value increased by 17.5% to €234.3 trillion (see annex, Table 2).[6] The individual shares of card payments, credit transfers, direct debits, e-money payments and the remaining payment services (cheques, money remittances and other payment services) in the total number of non-cash payment transactions for 2022 were broadly in line with the ones observed for the second half of 2022.
Data on payment servicesCard payments
In the second half of 2022 the number of card-based payments within the euro area increased by 13.5% to 35.8 billion compared with the previous six-month period. The corresponding total value of card-based payments rose by 14.3% to €1.5 trillion, reflecting an average value of around €41 per transaction. The split between remote and non-remote transactions in the total number of card payments was 17% to 83%, while the split in terms of value was 25% to 75%. The number of contactless card payments initiated at a physical electronic funds transfer point of sale terminal increased by 17.7% to 19.3 billion compared with the previous six-month period, with the corresponding total value rising by 20% to €0.5 trillion. At the national level, Portugal had the largest share of card payments as a percentage of the total number of non-cash payments in the second half of 2022, at around 75% (see annex, Table 3).
Credit transfers
In the second half of 2022 the number of credit transfers within the euro area increased by 5.1% to 13.4 billion compared with the previous six-month period, and the corresponding total value rose by 2.2% to €111.0 trillion. As higher-value payments are usually made by credit transfer, credit transfers made up 93.5% of the total value of non-cash payments. The relative importance of the number of credit transfers initiated electronically continued to increase, with the ratio of transactions initiated electronically to paper based transactions at around 21 to 1, while in terms of value the ratio was around 12 to 1. At the national level, Latvia had the largest share of credit transfers as a percentage of the total number of non-cash payments in the second half of 2022, at around 37% (see annex, Table 3).
Direct debits
In the second half of 2022 the number of direct debits within the euro area increased by 0.8% to 10.7 billion compared with the previous six-month period, and the corresponding total value rose by 14.4% to €4.4 trillion. Of the total number of direct debits, those with an electronic mandate accounted for 13% whereas those with consent given in other forms accounted for 87%, while in terms of value the split was 18% to 82%. At the national level, Germany had the largest share of direct debits as a percentage of the total number of non-cash payments in the second half of 2022, at around 36% (see annex, Table 3).
E-money payments
In the second half of 2022 the number of e-money payment transactions within the euro area increased by 8.2% to 4.5 billion compared with the previous six-month period, and the corresponding value rose by 12.2% to €0.3 billion. Of the total number of e-money payment transactions, those made with cards on which e-money can be stored accounted for 22% whereas those made with e-money accounts accounted for 78%, while in terms of value the split was 18% to 82%.
Cards and accepting devices
In the second half of 2022 the number of cards with a payment function increased by 3.8% to 704.8 million compared with the previous six-month period. With a total euro area population of around 345 million, this averaged two payment cards per euro area inhabitant.
In the second half of 2022 the total number of automated teller machines (ATMs) in the euro area decreased by 2.8% to 262,066. Of these, 27% accepted contactless transactions.
The number of point of sale (POS) terminals increased in the second half of 2022 by 7.7% to 19.6 million[7] compared with the previous six-month period. Of these terminals, 81% accepted contactless transactions.
Payment systems[8]
Retail payment systems
Retail payment systems in the euro area handle mainly payments that are made by individuals and businesses, with a relatively low value and high volume overall.
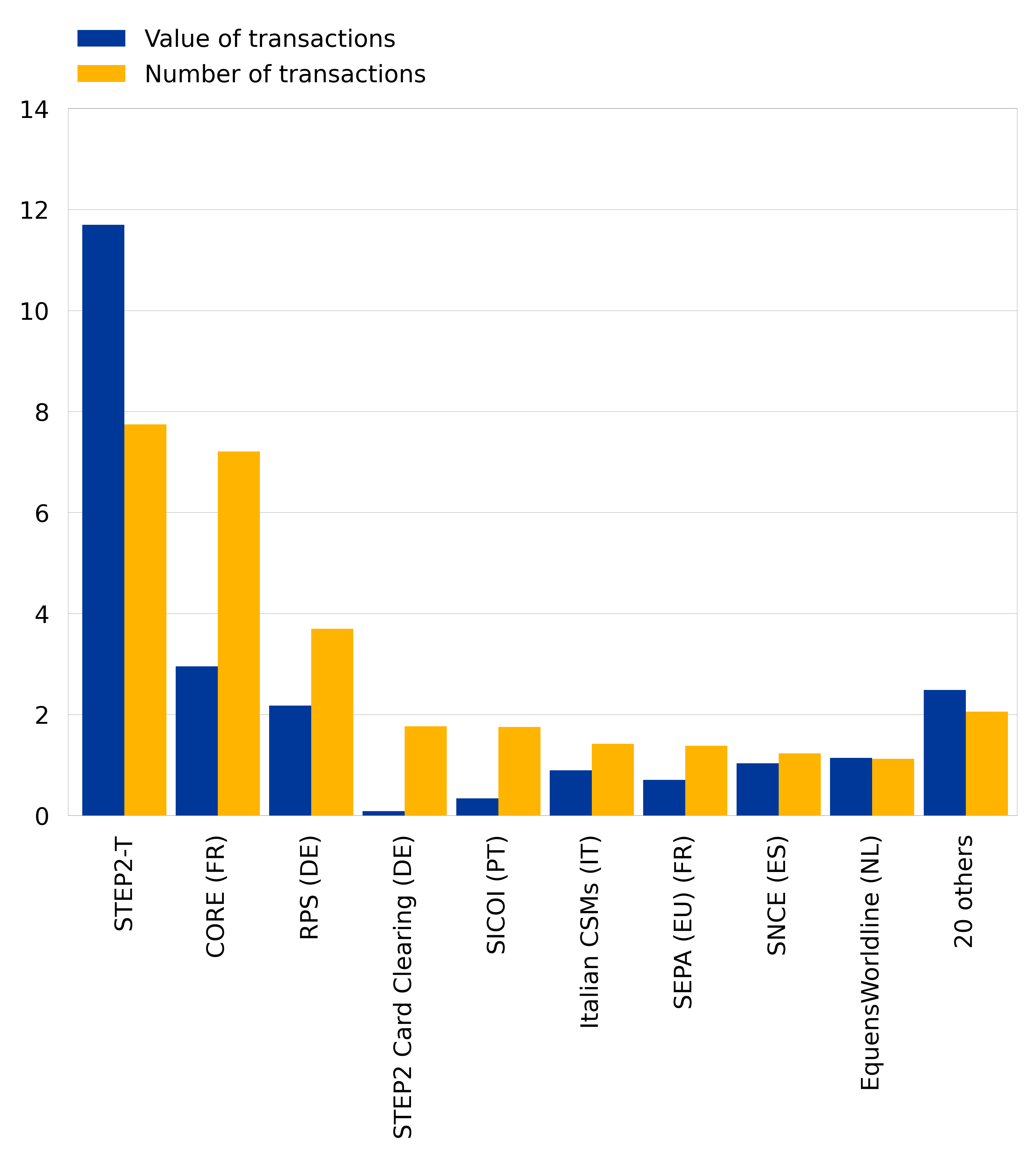
In the second half of 2022, 29 retail payment systems within the euro area processed around 29.4 billion transactions with a combined value of €23.5 trillion. Instant credit transfers accounted for 12% of the total number and for 4% of the total value of credit transfer transactions.
A high degree of concentration can be observed in euro area retail payment systems. The three largest systems (STEP2-T[9], CORE in France and RPS in Germany) processed 64% of the volume and 72% of the value of all transactions processed by euro area retail payment systems in the second half of 2022.
Chart 2 shows the number and value of transactions processed by the main retail payment systems in the second half of 2022.
Chart 2
Retail payment systems in the euro area in the second half of 2022
(value of transactions in EUR trillions and number of transactions in billions)
Large-value payment systems
Large-value payment systems are designed primarily to process large-value and/or high-priority payments made between system participants for their own account or on behalf of their customers. Although, as a rule, no minimum value is set for payments made through such systems, the average size of payments is usually relatively large.
In the second half of 2022, large-value payment systems settled 74.2 million payments with a total value of €333 trillion in euro payments, with TARGET2 and EURO1/STEP1 being the two main systems.[10]
Chart 3 shows the number and value of transactions processed by the main large-value payment systems in the second half of 2022.
Chart 3
Main large-value payment systems in the euro area in the second half of 2022
(value of transactions in EUR trillions and number of transactions in billions)

Notes:
- The full set of payment statistics can be downloaded from the ECB Data Portal (EDP). The EDP also includes interactive dashboards supporting data visualization. Detailed methodological information, including a list of all data definitions, is available under “Payment services and large-value and retail payment systems” in the "Statistics" section of the ECB's website.
- The methodological and reporting framework for payments statistics has been enhanced to take progressive developments in the payments market and related changes in the legal framework in Europe into account. The reporting requirements are set out in Regulation ECB/2020/59 amending Regulation ECB/2013/43 on payments statistics and in Guideline ECB/2021/13 on reporting requirements on payments statistics. In addition, the Manual on payments statistics reporting is available on the ECB’s website.
- Hyperlinks in the main body of the press release and in annex tables lead to data that may change with subsequent releases as a result of revisions. Figures shown in annex tables are a snapshot of the data at the time of the current release. Unless otherwise indicated, statistics referring to the euro area cover the EU Member States that had adopted the euro at the time to which the data relate.
Statistics are also collected for cheques, money remittances and other payment services, which together accounted for 2% of the total number of non-cash euro area payment transactions in the second half of 2022.
The published data have been collected in accordance with Regulation ECB/2020/59 amending Regulation ECB/2013/43 on payments statistics, which came into effect on 1 January 2022. Regulation ECB/2020/59 increased the frequency of data collection from annual to semi-annual. In the absence of semi-annual data for 2021, the analysis presented in this press release compares the first and the second halves of 2022. As of the next publication, the corresponding half year of two consecutive years (e.g. the first half of 2022 and the first half of 2023) will be compared in order to effectively account for seasonal factors. As this is the first publication under the new framework, all data should be treated as provisional and subject to revisions.
At the time of reporting the semi-annual data for 2022, some non-euro area EU countries were still in the process of implementing the requirements of Regulation ECB/2020/59. As such, EU aggregates do not cover all EU countries. Further information on which EU countries contributed to a specific EU aggregate can be found in the ECB Data Portal under the respective series key.
SEPA instruments are included in the respective categories. Information on these instruments can be found on the ECB's website.
Total non-cash payment services exclude cash-withdrawals and include credit transfers, direct debits, card payments with cards issued by resident payment service providers, e-money payment transactions with e-money issued by resident payment service providers, cheques, money remittances and other payment services. A wider total that includes cash withdrawals is also available on the ECB Data Portal.
Annual data for 2022 are derived by aggregating the first and the second halves of 2022.Owing to the increased frequency of payments statistics reporting (from annual to semi-annual) and the consequently higher data availability from reference period 2022 onwards, annual developments will become more peripheral in future press releases.
Due to national reporting specificities, the number of POS terminals reported for the first and second halves of 2022 is affected by double reporting in some euro area countries. As such, a big increase compared with the data for reference year 2021 is observed. This will be further investigated; corresponding figures may be revised.
Some of the payment systems in this press release are systemically important payment systems at euro area level. More information can be found on the ECB's website.
STEP2 is a pan-European automated clearing house for retail payments in euro operated by EBA CLEARING.
TARGET2 was the second-generation Trans-European Automated Real-time Gross settlement Express Transfer system. It was operated by the Eurosystem and settled payments in euro in central bank money until March 2023, when it was replaced by the new system, T2. EURO1/STEP1 is an EU-wide multilateral net large-value payment system for euro payments operated by EBA CLEARING. Payments are processed in EURO1 throughout the day and final balances are settled at the end of the day in TARGET2.
Europäische Zentralbank
Generaldirektion Kommunikation
- Sonnemannstraße 20
- 60314 Frankfurt am Main, Deutschland
- +49 69 1344 7455
- media@ecb.europa.eu
Nachdruck nur mit Quellenangabe gestattet.
Ansprechpartner für Medienvertreter

